There are many reasons to celebrate International Prosecco Day – but are researchers also raising a glass to one of Italy’s finest exports? Simon Linacre offers a quick taste of what we can learn from recent vintages of research outputs.
For many of us, prosecco seems to have become the sine qua non of any gathering, combining as it does the popping cork, light fizz and often considerable price benefit compared to champagne. Celebrated on 13 August each year, it offers a chance for prosecco producers to market their wines, and for the rest of us to, well, enjoy them!
But aside from the marketing fluff, what’s going on academically with prosecco? Dimensions and Altmetric – as well as being fantastically powerful tools to aid deep investigation of research topics – can also offer insight into almost any field of study. So, what can we glean from recent studies on prosecco?

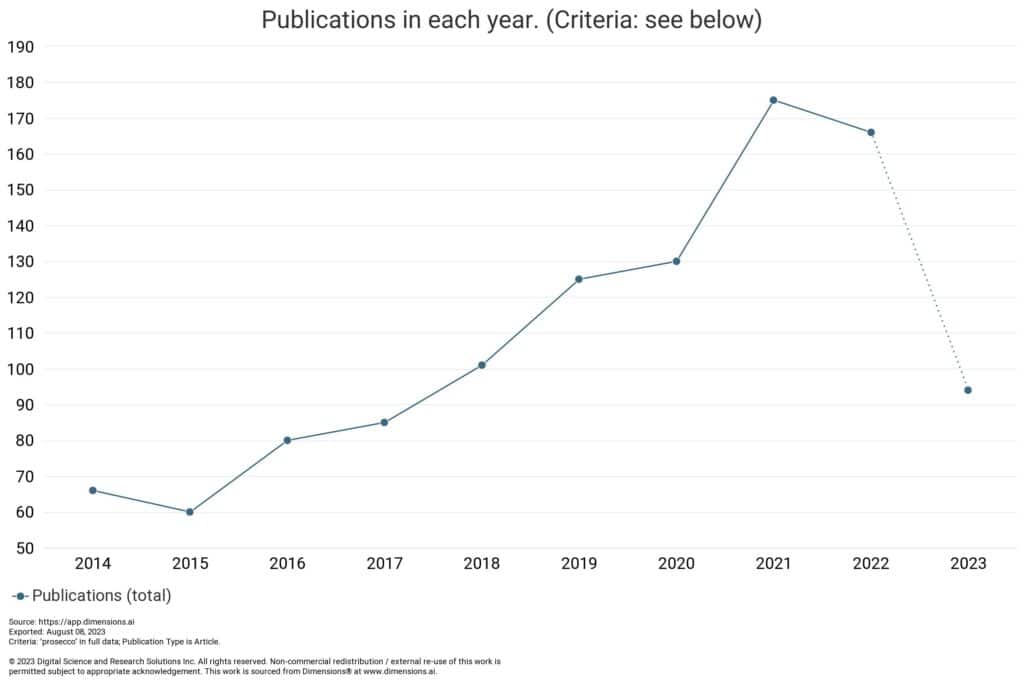
In Figure 1, we can see that the number of articles that mention ‘prosecco’ has steadily grown in the last decade, with a pronounced increase in 2021. However, this seemed to tail off in 2022, so perhaps interest in the topic has started to wane. This almost exactly mirrors global sales of prosecco and Italian wine in general, which have tailed off in 2022 after performing well during the pandemic.
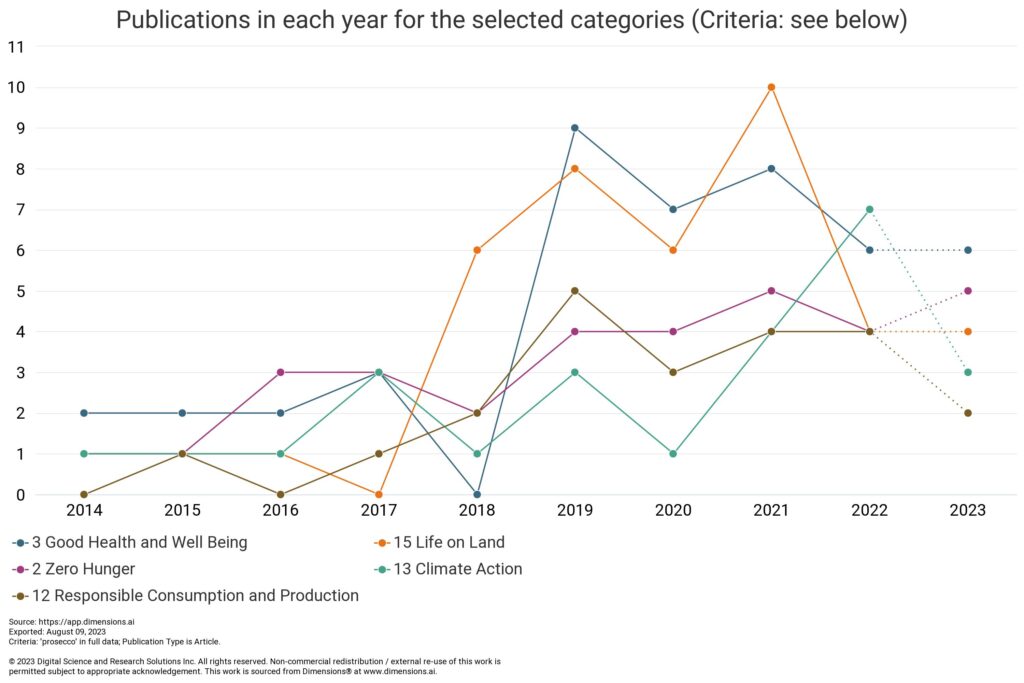
However, if we break it down by the number of articles published by Sustainable Development Goals – one of the most useful ways of delineating research on Dimensions – we can see that while there has been a drop in research related to Good Health and Well Being (SDG #3) and Life on Land (#15), there has been a marked increase in research on prosecco related to SDG #13, namely Climate Action. This perhaps reflects overall increased focus in this topic, particularly when related to food production where climate change is impacting on vines and crops, and any ability to meet increased demands.
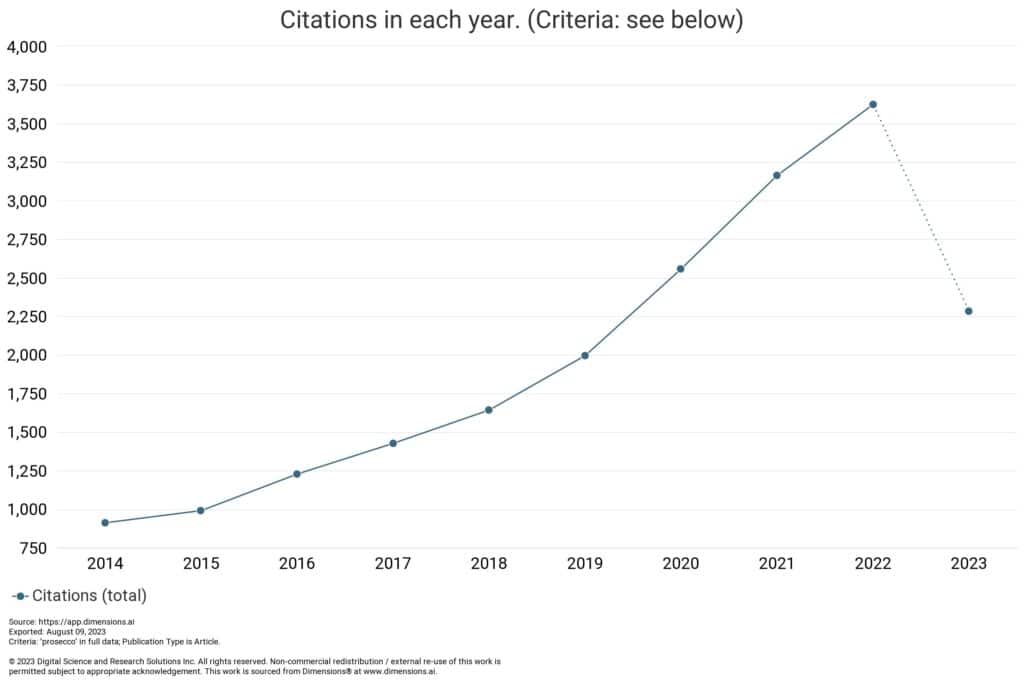
Certainly the reporting on prosecco-related research is maintaining its upwards trajectory, as we can see from Figure 3, which shows a steady increase in citations of research in this area. As there is a lag between citations and publications, we may see this drop away in future if the decline in research on prosecco remains on a downward trend.
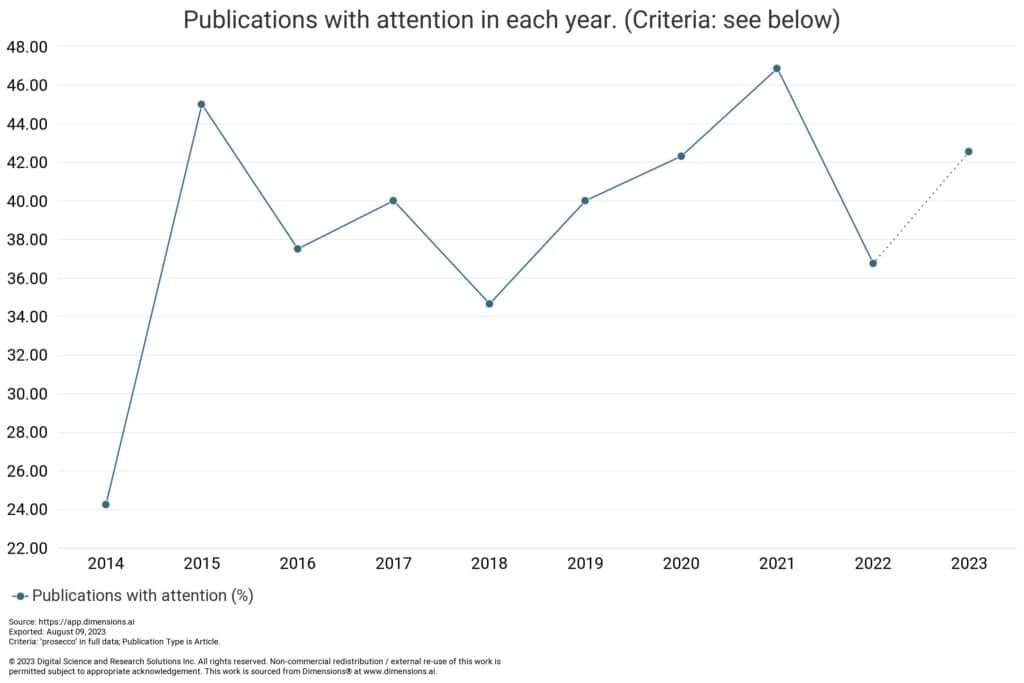
When we look at the influence of the research outside academia, we may have expected a similar continual rise, however data from Altmetric shows if anything a steeper decline than we saw in research output. This could be explained in part by the much shorter lead time that digital influence exhibits compared to citations, but it could also be a strong indicator that prosecco research has had its place in the sun, and academic interest has gone rather flat.
Request a demo or quote

About the Author
Simon Linacre, Head of Content, Brand & Press | Digital Science
Simon has 20 years’ experience in scholarly communications. He has lectured and published on the topics of bibliometrics, publication ethics and research impact, and has recently authored a book on predatory publishing. Simon is also a COPE Trustee and ALPSP tutor, and holds Masters degrees in Philosophy and International Business.
The post Has Prosecco research lost its fizz? appeared first on Digital Science.
from Digital Science https://ift.tt/lasFmeP
No comments:
Post a Comment