COVID-19, the disease caused by the pandemic coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, is primarily regarded as a respiratory infection. Yet the virus has also become known for affecting other parts of the body in ways not as well understood, sometimes with longer-term consequences, such as heart arrhythmia, fatigue and “brain fog.”
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine are using stem cell-derived organoids — small balls of human cells that look and act like mini-organs in a laboratory dish — to study how the virus interacts with various organ systems and to develop therapies to block infection.
“We’re finding that SARS-CoV-2 doesn’t infect the entire body in the same way,” said Tariq Rana, PhD, professor and chief of the Division of Genetics in the Department of Pediatrics at UC San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center. “In different cell types, the virus triggers the expression of different genes, and we see different outcomes.”
Rana’s team published their findings February 11, 2021 in Stem Cell Reports.
Like many organs, the team’s lung and brain organoids produce the molecules ACE2 and TMPRSS2, which sit like doorknobs on the outer surfaces of cells. SARS-CoV-2 grabs these doorknobs with its spike protein as a means to enter cells and establish infection.
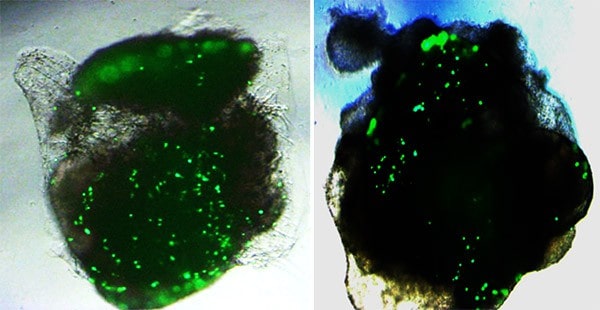
Rana and team developed a pseudovirus — a noninfectious version of SARS-CoV-2 — and labeled it with green fluorescent protein, or GFP, a bright molecule derived from jellyfish that helps researchers visualize the inner workings of cells. The fluorescent label allowed them to quantify the binding of the virus’ spike protein to ACE2 receptors in human lung and brain organoids, and evaluate the cells’ responses.
The team was surprised to see approximately 10-fold more ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors and correspondingly much higher viral infection in lung organoids, as compared to brain organoids. Treatment with viral spike protein or TMPRSS2 inhibitors reduced infection levels in both organoids.
“We saw dots of fluorescence in the brain organoids, but it was the lung organoids that really lit up,” Rana said.
Besides differences in infectivity levels, the lung and brain organoids also differed in their responses to the virus. SARS-CoV-2-infected lung organoids pumped out molecules intended to summon help from the immune system — interferons, cytokines and chemokines. Infected brain organoids, on the other hand, upped their production of other molecules, such as TLR3, a member of the toll-like receptor family that plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity.
Rana explained that, while it might seem at first like the brain organoid reaction is just another form of immune response, those molecules can also aid in programmed cell death. Rana’s team previously saw a similar brain cell response to Zika virus, an infection known to stunt neonatal brain development.
“The way we are seeing brain cells react to the virus may help explain some of the neurological effects reported by patients with COVID-19,” Rana said.
Of course, organoids aren’t exact replicas of human organs. They lack blood vessels and immune cells, for example. But they provide an important tool for studying diseases and testing potential therapies. According to Rana, organoids mimic the real-world human condition more accurately than cell lines or animal models that have been engineered to over-express human ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
“In animals over-expressing ACE2 receptors, you see everything light up with infection, even the brain, so everyone thinks this is the real situation,” Rana said. “But we found that’s likely not the case.”
In addition to their work with the pseudovirus, the team validated their findings by applying live, infectious SARS-CoV-2 to lung and brain organoids in a Biosafety Level-3 laboratory — a facility specially designed and certified to safely study high-risk microbes.
Now Rana and collaborators are developing SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors and testing how well they work in organoid models derived from people of a variety of racial and ethnic backgrounds that represent California’s diverse population. They were recently awarded new funding from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine to support the work.
Co-authors of the study include: Shashi Kant Tiwari, Shaobo Wang, Davey Smith and Aaron Carlin, all at UC San Diego.
Funding for this research came, in part, from the National Institutes of Health (grants CA177322, DA039562, DA049524, and AI125103), Burroughs Wellcome Fund and John and Mary Tu Foundation.
Disclosure: Tariq Rana is a founder of ViRx Pharmaceuticals and has an equity interest in the company. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
from ScienceBlog.com https://ift.tt/3uxfZJq

No comments:
Post a Comment